Explain the 3 Different Theories of Dna Replication.
It is because of the DNA Replication process that takes place during the S-phase synthetic phase of the cell division mitosis or meiosis in each and every cell. Primers are generated by the enzyme DNA primase.
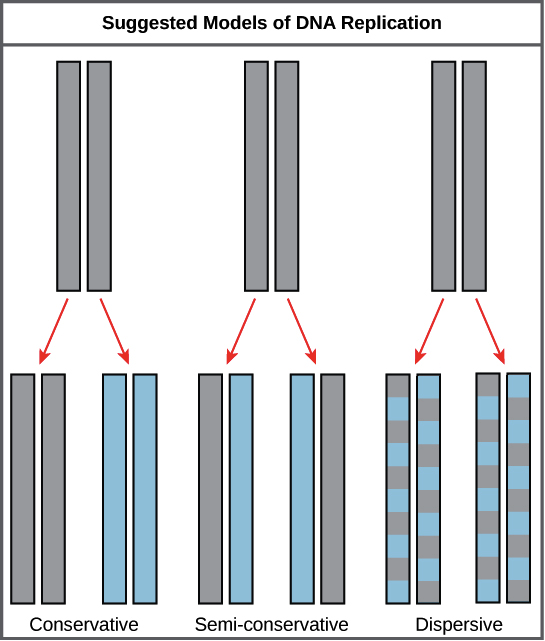
In the semi-conservative model the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself.

. The opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands the priming of the template strand and the assembly of the new DNA segmentDuring separation the two strands of the DNA double helix uncoil at a specific location called the origin. There are three postulated methods of DNA replication. Which theory was proven to be correct.
Three modelstheories of DNA replication. In this model the two strands of DNA unwind from each other and each acts as a template. What are the basic building blocks of DNA called.
The Dispersive Model describes the original DNA breaking apart and the newly synthesized DNA molecule being made partly of. Start studying DNA Replication Bozeman Video. - Semi-Conservative DNA splits in half and on each.
The arrow points from the 5 to the 3 end of the polynucleotide. Which theory was proven. The opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands the priming of the template strand and the assembly of the new DNA segment.
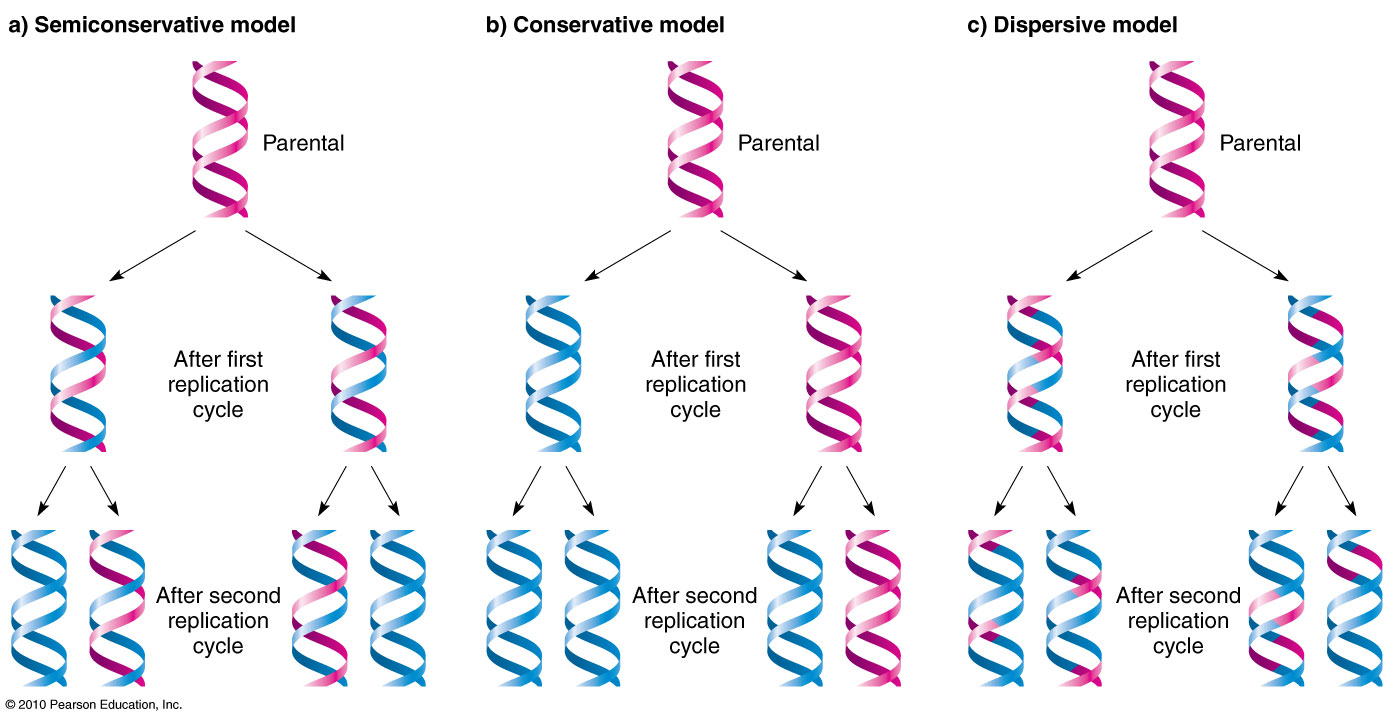
After one round of replication the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand. Explain the 3 different theories of DNA replication. There are three important experiments which support that DNA replication is semi-conservative.
It also discuss about the evidences for semi-conservative replication. 2 DNA helicases and single-strand DNA-binding SSB proteins to help in opening up the DNA helix so that it can be copied. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Among these three conservative and dispersive replication is not found to be biologically significant. Semi-conservative conservative and dispersive replication. In all models the DNA that is labeled by a short period of synthesis is indicated by a thin line.
In the conservative model the first replication produces one daughter molecule containing both parental strands and another containing all new strands. New strands go back together. What is Conservative Replication 3.
Namely semiconservative replication conservative replication and dispersive replication. The primer always binds as the starting point for replication. 1 Dispersive 2 Conservative and 3 Semi-conservative.
Yoobin Chu Darwin Bozeman Video Guide. Overview and Key Difference 2. B The knife-and-fork model.
In this model DNA replication results in one molecule that consists of both original DNA. There are three models that describe DNA replication in living organisms. The Semi-Conservative Model describes the double stranded DNA molecule separating and each strand replicates.
1 Watson and Crick even suggested that DNA was possibly replicated without proteins wondering whether a special enzyme would be required to carry out the polymerization or whether the existing single helical chain could act effectively as an. After replication the single daughter molecules contain a strand of the original parent molecule and a new strand. They are conservative replication semiconservative replication and dispersive replication.
Semi-Conservative Conservative Dispersive models of DNA replication. Explain the process of DNA replication. In the dispersive model DNA.
After Watson and Crick proposed the double helix structure for DNA three models for DNA replication were proposed. 3 DNA ligase and an enzyme that degrades RNA primers to seal together the discontinuously synthesized lagging-strand DNA fragments. Replication occurs in three major steps.
DNA replication the process of copying DNA has three different models to explain its processes the most well-known of which is the Meselson and Stahl model. C The rolling circle model. Then Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl conducted the Meselson-Stahl experiment which returned results that supported the semi-conservative theory of.
Theory that says old strands go back together. What does anti-parallel mean in DNA. These include 1 DNA polymerase and DNA primase to catalyze nucleoside triphosphate polymerization.
A THEORY OF DNA REPLICATION 489 quently joined together. Explain the 3 different theories of DNA replication. Theory that says the strands of the daughter DNA molecule contain pieces of parental.
Replication occurs in three major steps. Obtaining evidence for scientific theoriesMeselson and Stahl obtained evidence for the semi-conservative replication of DNA. Conservative replication produces one helix containing entirely old.
Explain the 3 different theories of DNA replication. Conservative semiconservative and dispersive. What does 5 to 3 mean in DNA.
By 1957 three theories about DNA replication prevailed. For some time it was believed by some molecular biologist that life originated with the appearance of the first DNA molecule. The different types of DNA polymerase do not need to be distinguished.
View DNA_Replication_Bozeman_Video_Guide_ from BIO 102 at Lehman College CUNY. There are three possible ways of DNA replication. - Semi-Conservative DNA splits in half and on each side a new DNA is formed - Conservative first DNA remains intact and makes a photocopy of itself - Dispersive chunks of DNA were being split between the two.
See text for details. Note that after two rounds two of the DNA molecules consist only of new material while the. Once the DNA strands have been separated a short piece of RNA called a primer binds to the 3 end of the strand.
Describe how the Meselson and Stahl experiment proved that theory. The leading strand is the simplest to replicate. The three possible ways are.
D The prefork replication model.

7 2 Semi Conservative Dna Replication Biology Libretexts
Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy


Comments
Post a Comment